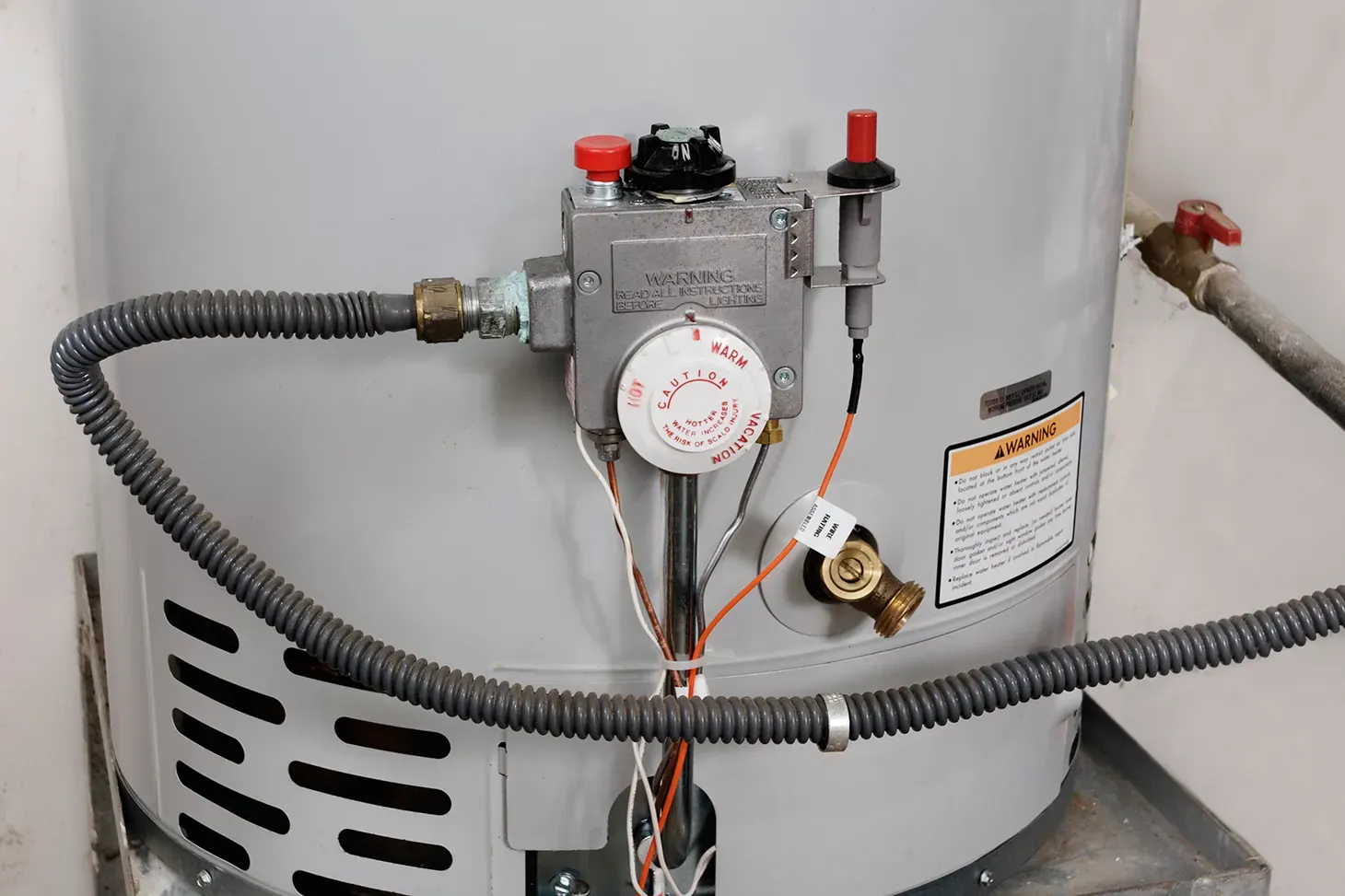
Water Heaters, Water Heater Repair, Water Heater Installation & Maintenance And Related Services
Get the Service You Want and Need!
Quick Category Links for Water Heaters
When you need water heater repairs, water heater installations, or water heater maintenace, you can count on Able Plumbing.
This is a great place to start to discover information about water heaters, getting hot water back up and running in your home, new water heater installations, water heater maintenance, and other topics related to circulating hot water throughout your home. If, after reading all about your water heater options, you are still stuck, have questions or just plain don't want to deal with it yourself, please reach out and call us. At Able Plumbing, we are expert plumbers with over 35+ years of local plumbing experience in Chico and surrounding cities and counties in Northern California. We're highly rated by your friends and family and ready to help you solve your hot water problems!
When it comes to choosing and maintaining water heaters, you have many choices available.
Natural Gas Water Heaters
These energy efficient models provide hot water faster than most electric water heaters. This gives cost-efficient operations while producing fewer greenhouse gasses than other fossil fuels.

Electric Water Heaters
Though not as cost effective as using gas, electric water heaters can offer some installation benefits especially when access to gas lines is not economically feasible to the installation. Sometimes, these types of water heaters find great usefulness in commercial installations where smaller tanks capacities can be used.
Propane Water Heaters
Propane offers an alternative gas water heater for areas lacking natural gas lines, primarily in rural areas. These types of water heaters also offer cost-efficient operation options.

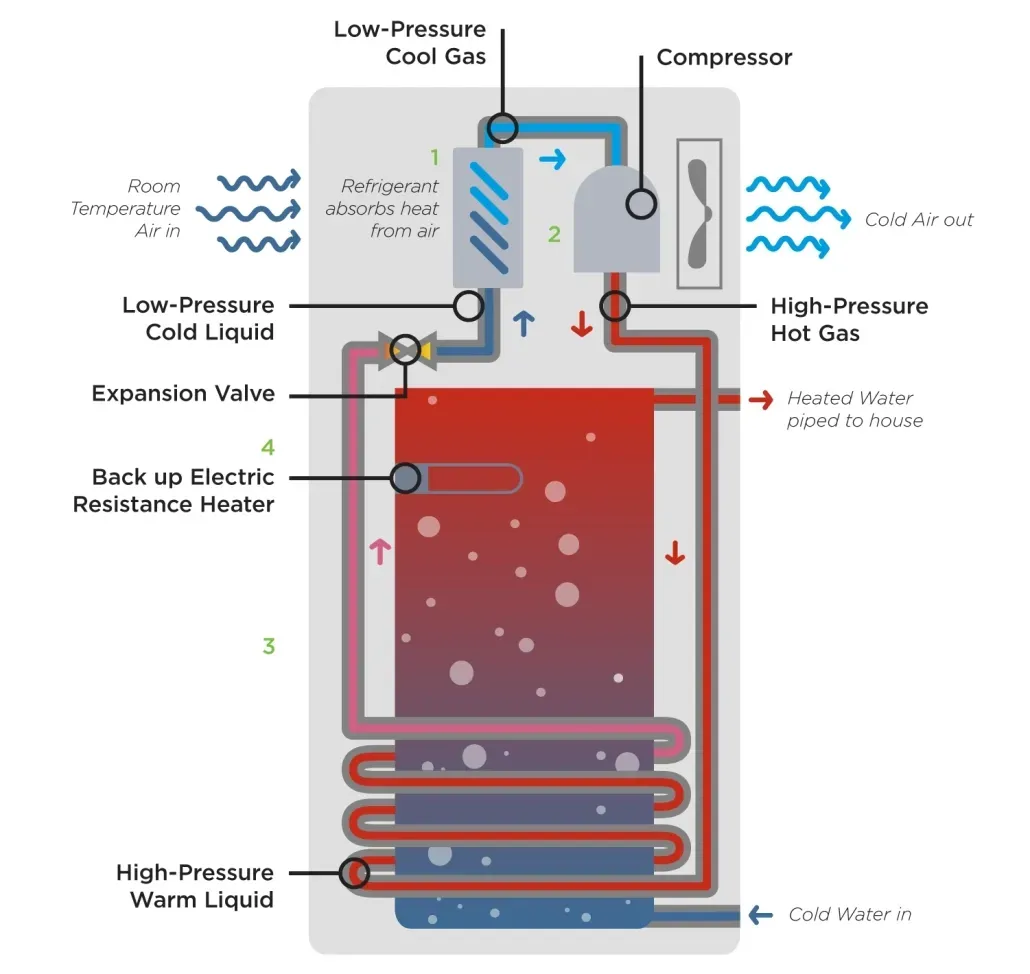
Heat Pump Water Heaters
Two to three times more energy-efficient than conventional electric resistance water heaters, this can lead to considerable energy and cost savings over time. Heat pump water heaters, also known as hybrid water heaters, operate on the principle of heat transfer rather than direct heating.
Tankless Water Heaters
Tankless water heaters offer the promise of endless hot water running through your home or business. Though installation of these water heaters can be expensive, not having to wait for hot water has been said to be well worth it. These types of water heaters can be gas or electric.
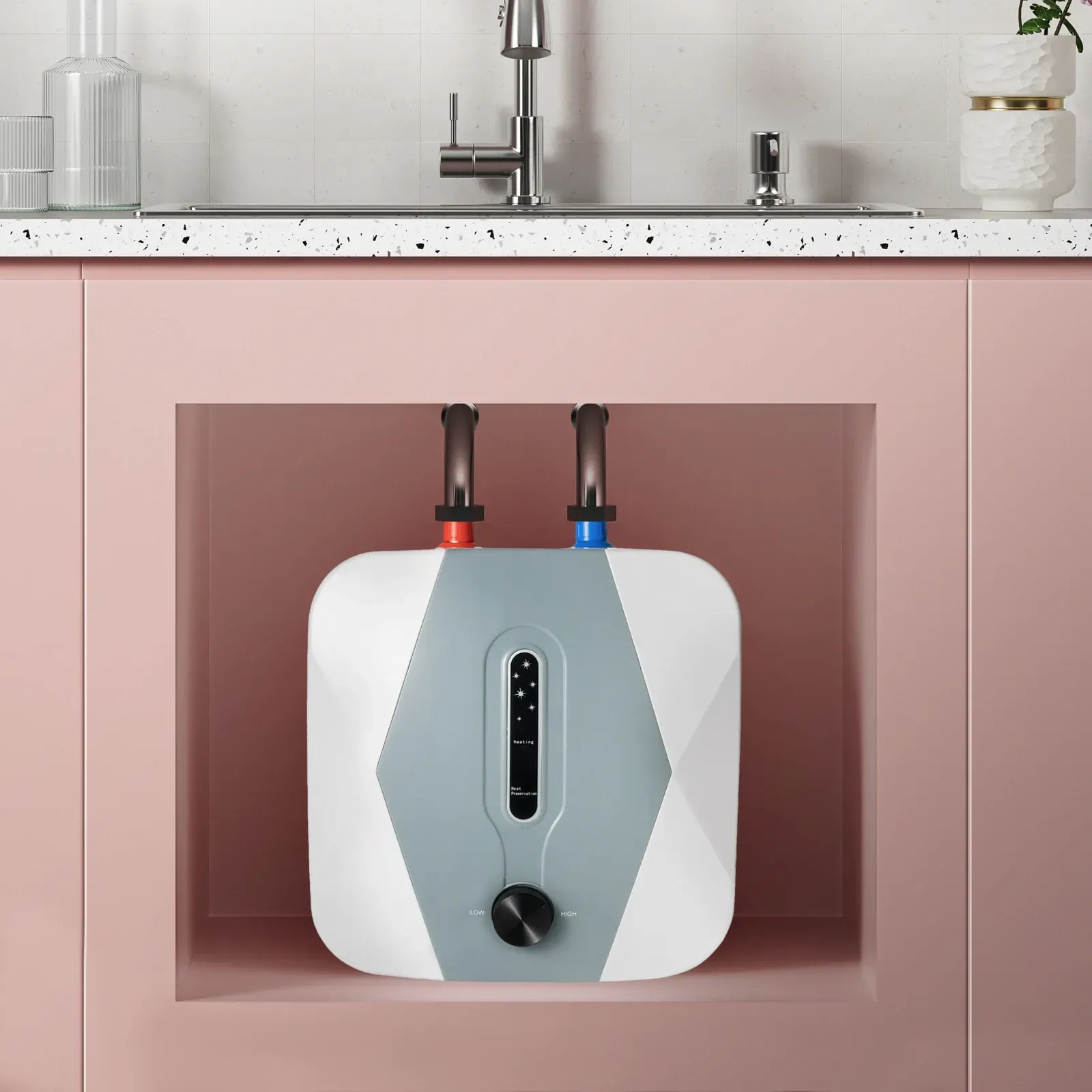


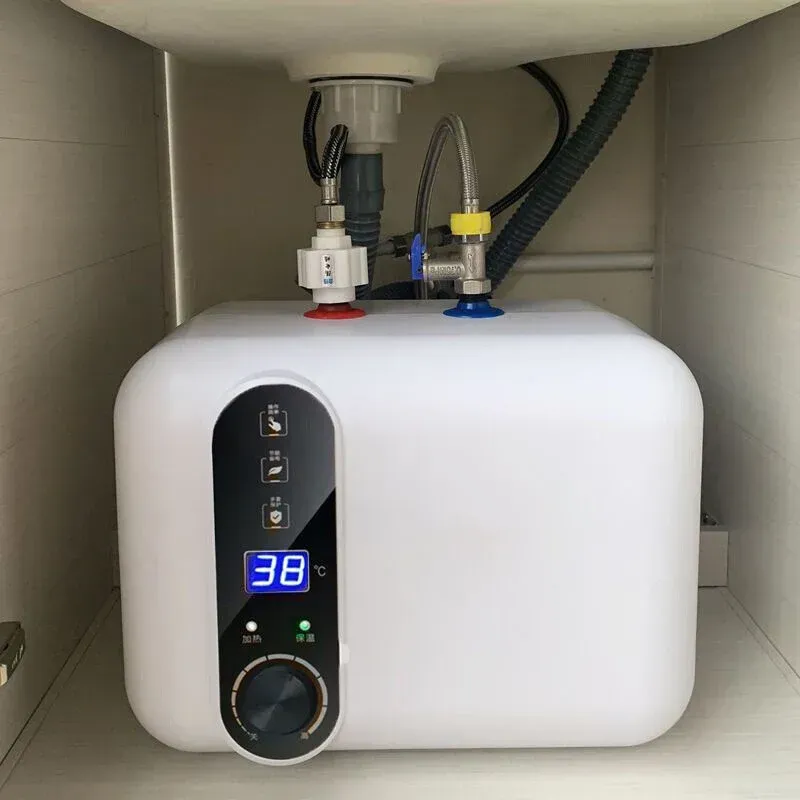
Under Sink Water Heaters
These types of water heaters offer convenience in tight spaces like bathrooms and kitchens. They come in tankless models as well as mini-tank water heater models. Find the capacity and flow rate that works for your needs.
Insta-Hot Water Heaters
- Energy Efficiency: By heating water only when it's needed, instant hot water heaters can be more energy-efficient than traditional tank models, leading to lower utility bills.
- Water Savings: With a unit such as this, it will effectively eliminate the need to let the water run at the sink while waiting for it to get hot, creating water conservation of many gallons over a year.
- Cost Effective:Instant hot water heaters typically are more cost effective than a recirculation line especially if your hot water needs are smaller and/or mostly needed at one particular sink.

Alongside Water Heaters, There Are Other Systems In Your Home Related To Keeping Hot Water Flowing
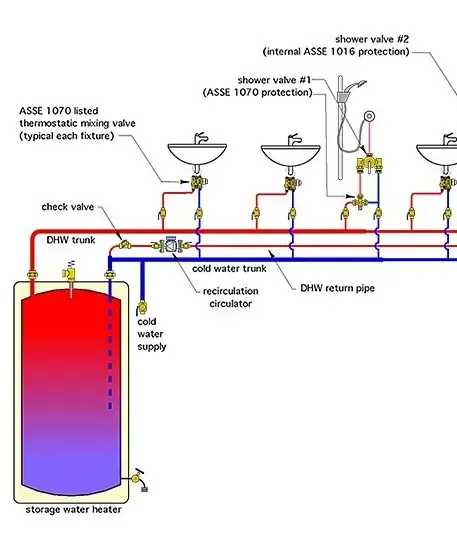
Recirculation Lines
A recirculation system continuously pumps water from the water heater through the hot water pipes with a pump mechanism and back to the heater via a dedicated return line or through the cold water line with a specific valve. This loop keeps hot water moving and readily available at all points of use. Some systems activate on demand, using a switch or motion sensor, while others operate on a timer to ensure hot water availability during known peak times.


Water Temperature and Pressure In Your Home
High Temperature: Setting the water heater temperature too high can lead to scalding injuries and increase energy consumption. The recommended setting for most households is around 120°F (49°C), which balances safety with the need to kill bacteria and minimize energy use.
Excessive Pressure: Water pressure that is too high can stress the water heater and plumbing fixtures, leading to leaks or tank failure. Pressure issues often arise from thermal expansion as heated water increases in volume. If you are experiencing issues in your home with temperature, pressure, or both, you'll want to quickly call the plumbing experts at Able Plumbing to come take a look.
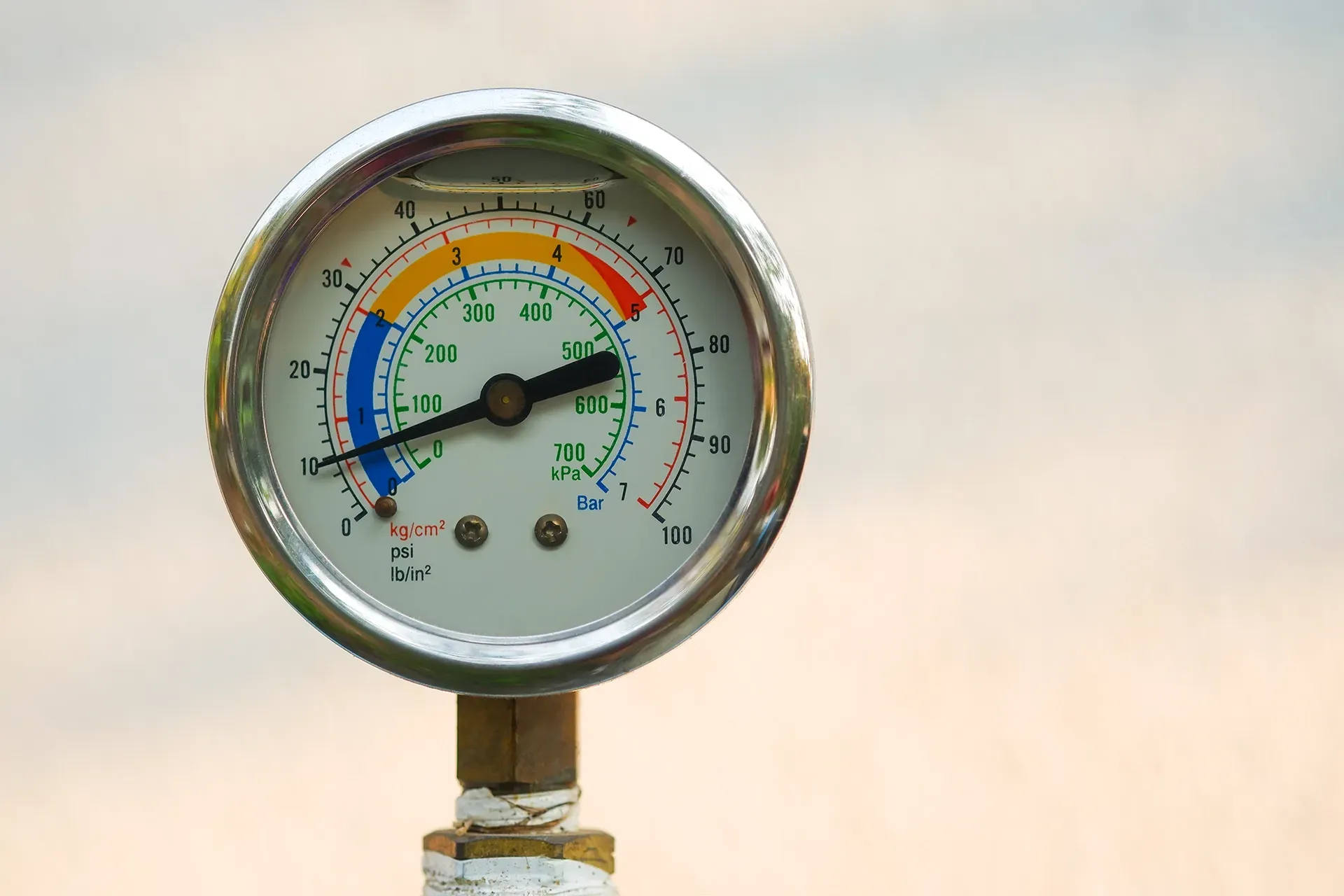

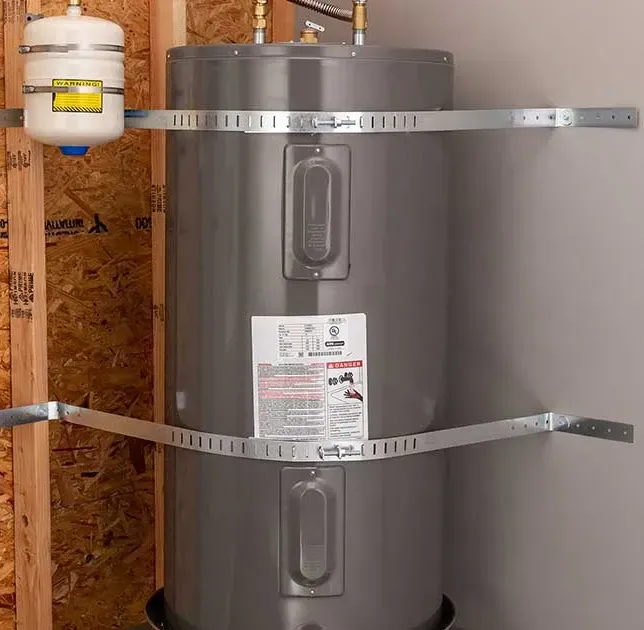
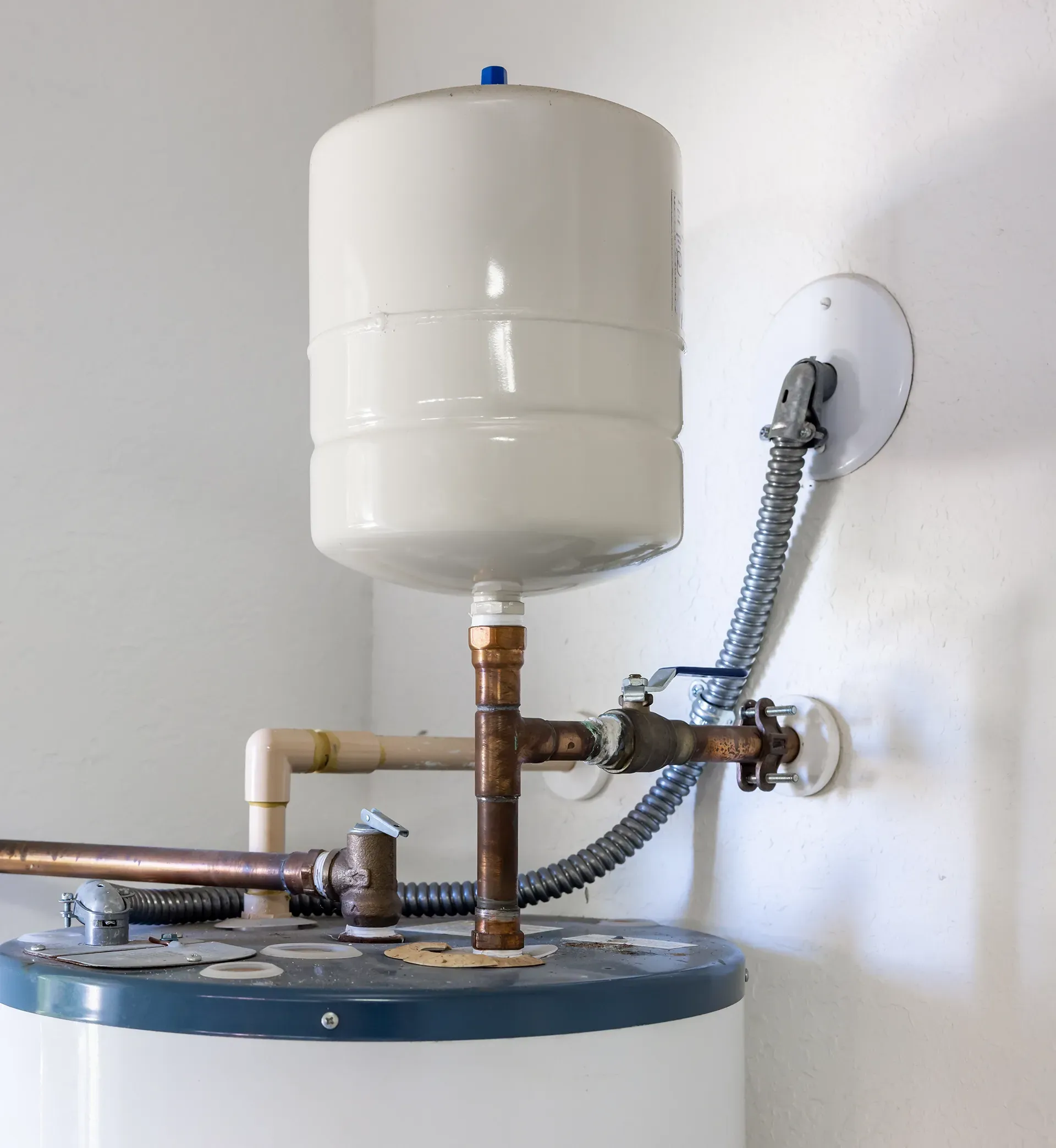
Expansion Tanks and Their Role in Hot Water Heater Systems
- Protection Against Overpressure: By accommodating the expanded volume of water, expansion tanks prevent overpressure in the system, protecting against leaks in water heaters, ruptured pipes, and damaged valves.
- Compliance with Building Codes: Many regions require the installation of expansion tanks in new construction or when replacing a water heater, especially in closed-loop systems where backflow into the municipal water supply is prevented by a check valve or pressure reducing valve, usually near the meter.
- Enhanced System Longevity: By mitigating pressure fluctuations, expansion tanks contribute to the extended lifespan of water heaters and reduce the likelihood of premature system failure.
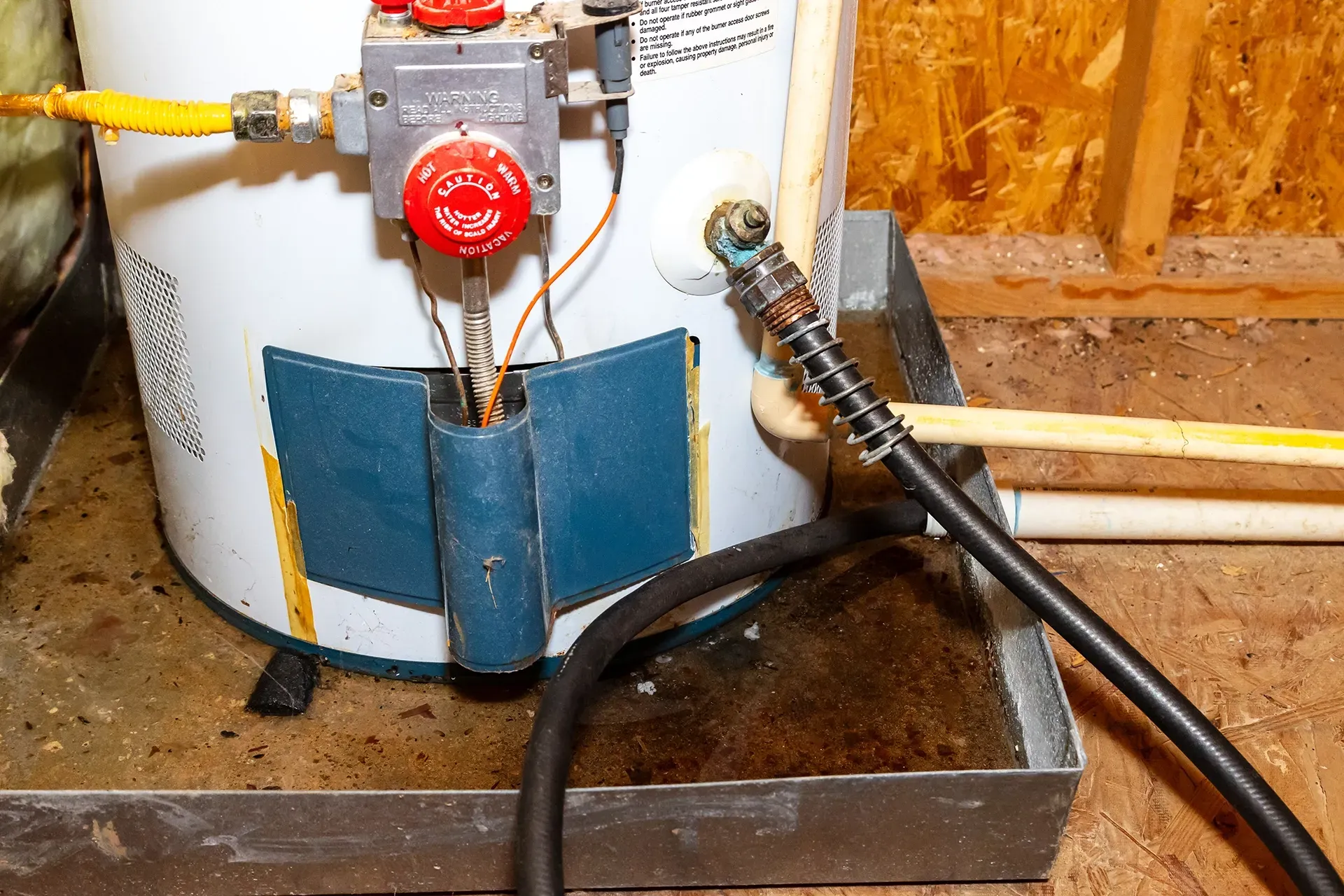


Why You Should Have A Drain Pain For Your Water Heater
- Leak Protection: Over time, water heaters can develop leaks due to corrosion, sediment buildup, or pressure issues. A drain pan collects this water, helping to prevent it from spreading and causing damage.
- Compliance with Building Codes: In many jurisdictions, installing a drain pan under water heaters, especially those located in attics or in closets inside the living spaces, is required by building codes.
- Peace of Mind: Knowing that pans will help to contain leaks provides owners with peace of mind, especially when the water heater is located in areas not regularly checked for leaks.
Why Should I Use A Water Heater Stand?
- Safety: The primary function of a water heater stand is to enhance safety by elevating the ignition source of gas water heaters, reducing the risk of flammable vapors being ignited.
- Flood Protection: In areas prone to flooding, raising the water heater can prevent water damage to the unit, prolonging its lifespan and ensuring continued operation.
- Compliance with Building Codes: Many local building codes require gas water heaters in garages and similar locations to be elevated, typically at least 18 inches off the ground, to meet safety regulations.
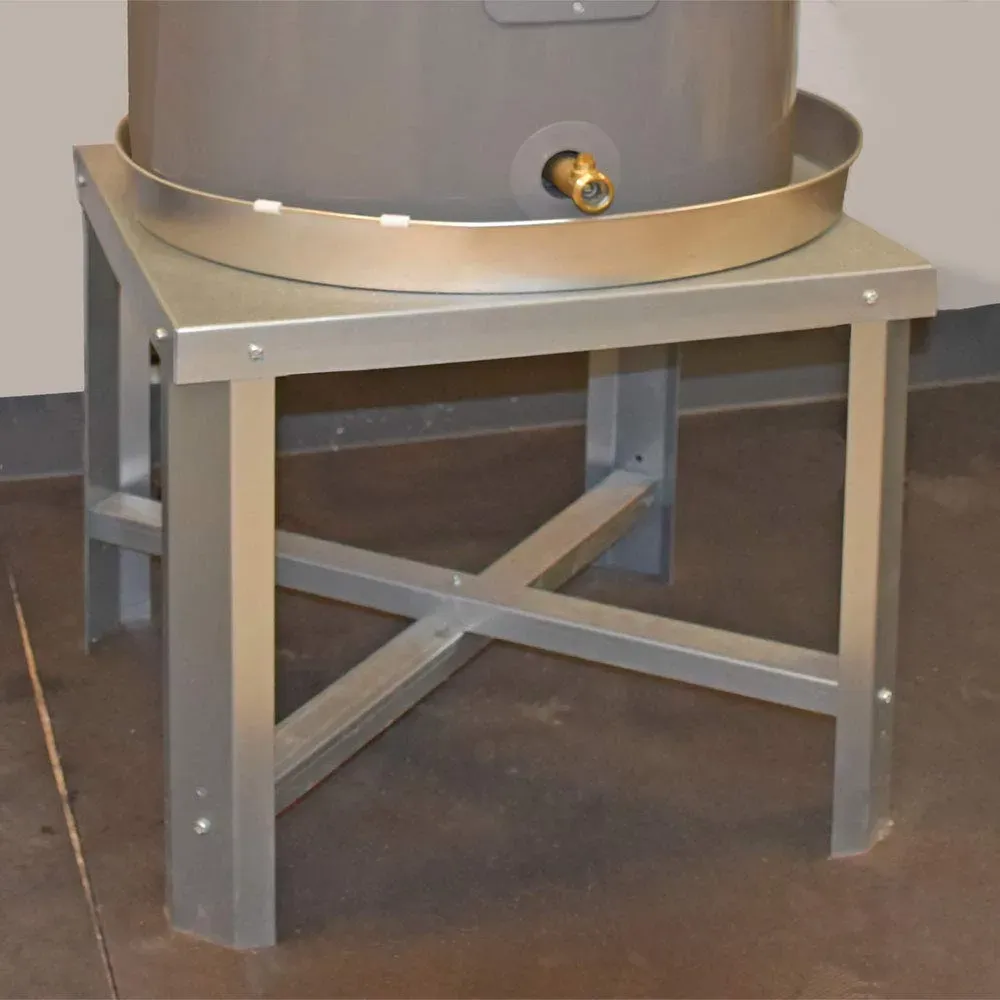

The Importance of Annually Inspecting Your Hot Water Heater
Visual Inspection: Annually inspect your water heater for signs of wear or damage, such as rust, corrosion, or water leakage around the base of the tank or in piping connections for traditional water heaters. For tankless models, check for any error codes or warning lights that may indicate a problem. There are several areas to check. You can further go into detail on this topic by clicking the button below.
Problems With Your Water Heater? Let's Look At Troubleshooting The Cause
Not having hot water in the home is a big issue and needs immediate attention. Please call us right away to help troubleshoot what is going on. If you are experiencing any of the following, it's time to give us a call:
- No Hot Water
- Insufficient Hot Water or Hot Water Running Out Quickly
- Water Is Too Hot
- Low or High Pressure Issues
- Noisy Water Heater